...
This general ledger supports multiple GAAPs in parallel. For each GAAP it can be decided if the implementation should cover a
...
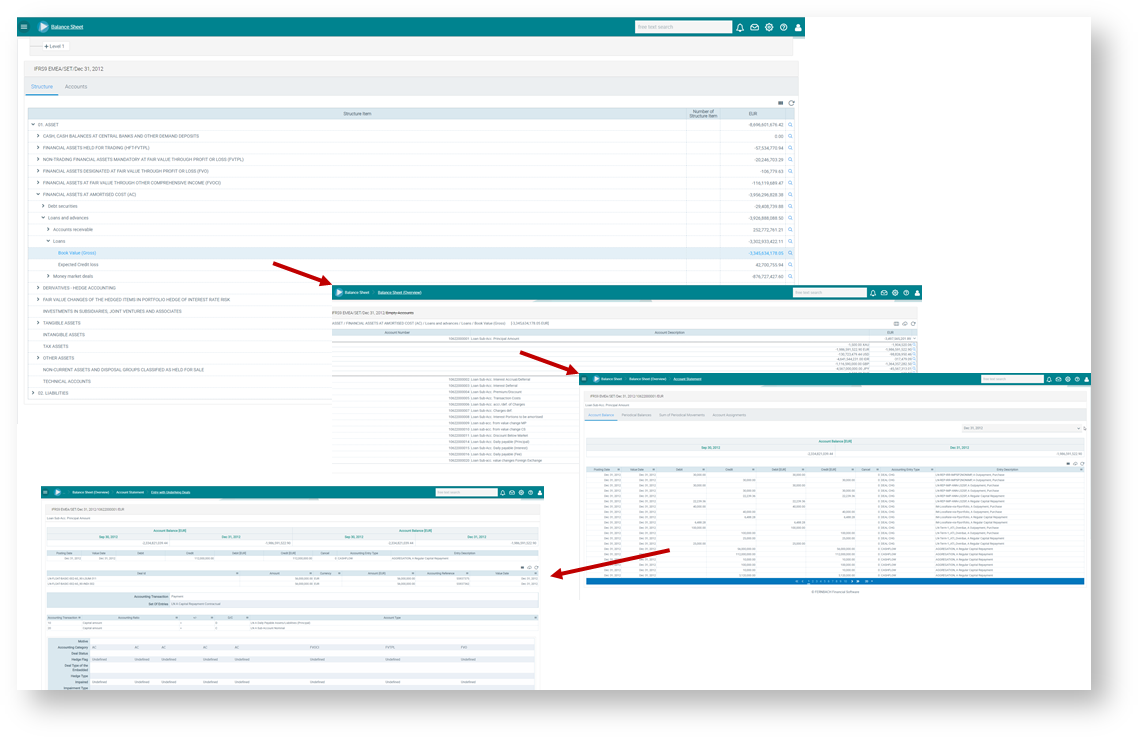
Figure: Drilldown from general ledger account balance
A
...
- All financial instruments and
- All non-financial instruments as well as
- All valuation elements
As such, a full-size general ledger reflects the entire business of an entity.
It provides specific general ledger functionalities such as
- valuation of account balances in FX and posting of the related FX result
- profit and loss zeroisation at the end of a configurable fiscal period
Beside comprehensive financial statements, the functionality includes the support of analysing, reporting and presentation requirements.
A shadow ledger concentrates on an excerpt of the business of an entity. This excerpt can be for example "All financial instruments" or a "Loan Ledger".
...
The decision which implementation type of a general ledger in FlexFinance fits best should include the following aspects:
- No third-party general ledger is in place
- A third-party general ledger is in place, but
- does not support the drilldown of general ledger account balances to individual deal level (often third-party general ledgers work at aggregated level only)
- does not support the breakdown of account balances to freely definable portfolios (often third-party general ledgers are limted to 3 to 5 criteira which can be used for drilldown)
...
General Ledger consists of
- Balance Sheet
- Profit and Loss
- Chart of Accounts
It can deal with
- Multiple GAAPs in parallel (The General Ledger contains a separate chart of accounts for each GAAP)
- Multiple tennants (The General Ledger supports consolidated views)
- Multiple currencies (The General Ledger keeps all bookings in original transaction currency as well as in functional currency)
The General Ledger
- Allows analysis at account, product, customer, business and project level with results aggregated at account / cost center level.
- Allows more accurate and efficient product control as entries are made at detailed and consolidated levels.
- Enables easier automation of reconciliation with minimal manual intervention as detailed or transaction-based data can be tracked and analysed in multiple dimensions.
In a multi-GAAP environment, it is possible to run e.g. a full-size general ledger for IFRS and a shadow ledger light for local GAAP which focusses on the specific valuation elements for a specific portfolio.
There are various options available for integrating the general ledger into the entire solution architecture:
- Full-size general ledger: as such it contains the full balance sheet (statement of financial positions) as well as the profit and loss account (income statement). It can accommodate financial instruments as well as non-financial instruments.
- Shadow ledger: as such it is limited to financial instruments or even a selected product portfolio only (e.g. loan ledger)
- Shadow ledger light: as such it is limited to financial instruments or even a selected product portfolio only (e.g. loan ledger) and in addition it only covers an excerpt of valuation elements for the relevant portfolio (e.g. it only covers entries related to the valuations of loans)
The main difference between the shadow ledger options is which analysis and evaluation functions can be provided at single transaction level for the audit trail for the general ledger account balances and revenues.
If the tool is supposed to provide comprehensive analysis and evaluation options, it should be implemented as a shadow ledger or general ledger.
If the solution is implemented as a shadow ledger or shadow ledger light, a third-party tool needs to be installed as a general ledger. This external ledger can be fed with debit/credit entries. A specific data mart exists for this purpose.
The implementation of the tool as a general ledger must be consistent with the use of an additional third-party general ledger. Usually the drilldown and analysing functionality of the solution exceeds by far the capabilities of third-party ledgers. Therefore it might be reasonable to use the solution as a general ledger while keeping an existing external general ledger in place for specific requirements such as legal reporting (that is not saying that the solution is not capable to also deal with this requirement, but maybe to keep existing tools in place for several reasons at a certain point of time).
General ledger account balances are based on debit/credit entries.
Sources for debit/credit entries can be
- Import of credit/debit entries at general ledger account level
- Accounting Rules Engine