...
Regulatory obligations impact business in various ways. For compliance purposes, business processes need to be adjusted and new control mechanism mechanisms need to be implemented. While supporting compliance as well as the necessary processes, FlexFinance helps to professionalise business and achieve economic benefits.
...
The expected credit loss (ECL) for an existing transaction are is calculated during regulatory analysis and posted to risk provisioning with an immediate effect on income. When ECL expectations later become reality, the provision for credit risks is written back at the expense of a write-down without any impact on the P&L at this point in time.
On the other hand, an attempt is made from an economic point of view, to limit the "feared" ECL is attempted to be limited credit loss operationally and thus starts to start with the loan application or is integrated to integrate it into credit management as an early warning system. From a business perspective, it is all about credit risk and how to consider it in:
...
The regulatory ECL, as well as parameters used while calculating ECLs, can be reused in the an economic business environment.
...
- Staging
IFRS 9 differentiates between 3 stages depending on the significance of the deterioration in credit quality. Depending on the stage assigned, IFRS 9 calls for the consideration of 12-month or lifetime ECLs.
As far as early warning is concerned, the differentiation between the 3 stages does not have a sufficient degree of fine granularity. For example, it makes a difference in the probability of default from the perspective of the individual deal if a retail customer is delayed with a due payment for 5 days, 2 weeks or even 4 weeks. Even the probability of success of forbearance or modification measures depends on the right timing which is not necessarily provided by regulatory approaches. - Segmentation
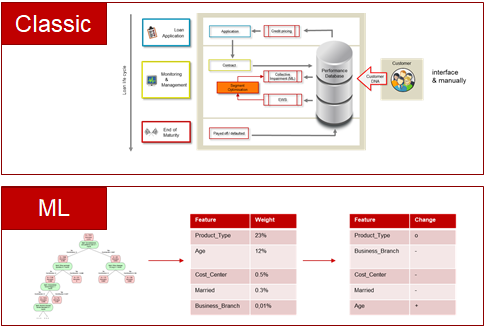
Conventional approaches work with a rule-based segmentation, applying manually captured settings to identify similar credit risk characteristics using an excerpt of the customer DNA and some product and deal-specific parameters. The calculation of lifetime expected credit losses using parameters based on portfolio/segment, defined using high level similar credit risk characteristics, is fine. However, e.g. for significant deals, the use of regulatory segments to decide on a credit risk adjusted price is questionable. Due to the rough granularity of segments, an entity might not make a deal because the interest offered was too high or it might conclude a deal where the interest does not cover the credit risk.
...
Figure: Segmentation in the conventional approach and machine learning
Macroecnomic Macroeconomic parameters
The macroeconomic parameter is Macroeconomic parameters are forecasted separately in the conventional approach. Then the parameter forecasted is used as input for the Roll Rate or Migration Analysis.
In the machine learning approach, the forecast of the macroeconomic parameter is integrated into the machine learning process of the neuronal network.
Conventional approaches are sufficient and accepted for regulatory requirements. Of course, they can also be generally used for business analysis too. |
...