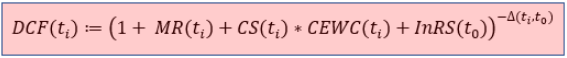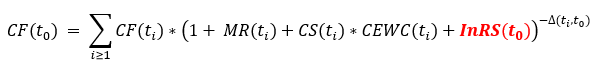The Fair Value DCF is calculated based on the discounted cash flow method. This method takes into consideration all risks associated with financial instruments. These include:
- cash flow timing and variability,
- benchmark market rate risks,
- credit risk (captured through credit spread),
- credit risk mitigation instruments,
- risk of embedded options (captured either through option pricing models or on a retail portfolio level through e.g. prepayment curves),
- liquidity and operational costs (acquired through an initial residual spread incorporated in the discount rate).
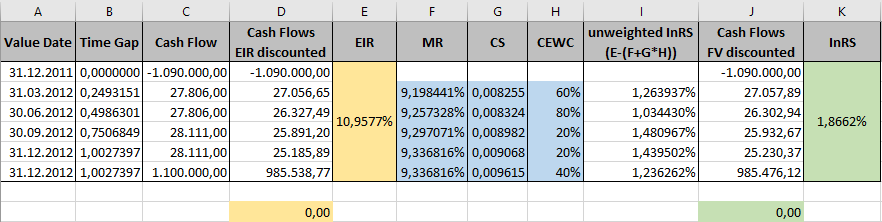
The discounted cash flow method derives the fair value of a loan at time t via
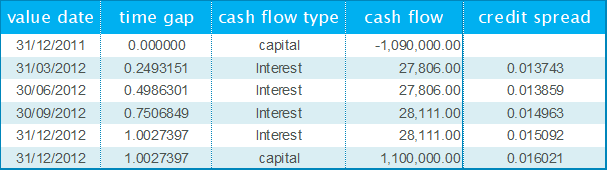
where CF(ti) are the expected future cash flows of the loan. A fair value calculated with the discounted cash flow method differs from the classical present value through the rates used in the discounting: While the classical present value only incorporates the market interest rate, the discount factor DCF(ti) incorporates all of the following elements:
- market interest rate
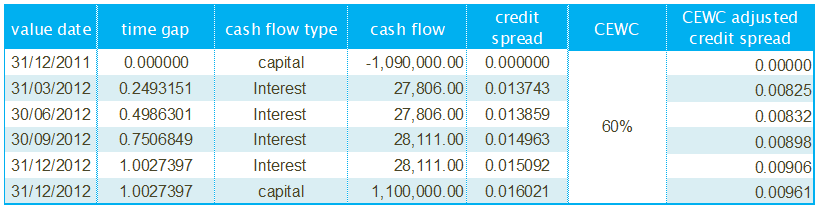
- credit spread and collateral enhancement weighting coefficient
- initial residual spread
To be more precise, the discount factor at payment date ti used in the calculation of fair value is obtained by
where
- MR(ti) denotes the market interest rate at payment date ti,
- CS(ti) stands for the credit spread of the counterparty at payment date ti,
- CEWC(ti) denotes the collateral enhancement weighting coefficient of the deal at payment date ti,
- InRS(t0) stands for the initial residual spread of the deal conclusion date t0 and
- Δ(ti,t0) denotes the time gap between payment date ti and deal conclusion date t0.
Deriving the fair value using the above formula for the discount factor leads to the calculation of a fair value.
Please find below additional information regarding the following topics: