In general, IFRS 9 differentiates between 3 accounting categories:
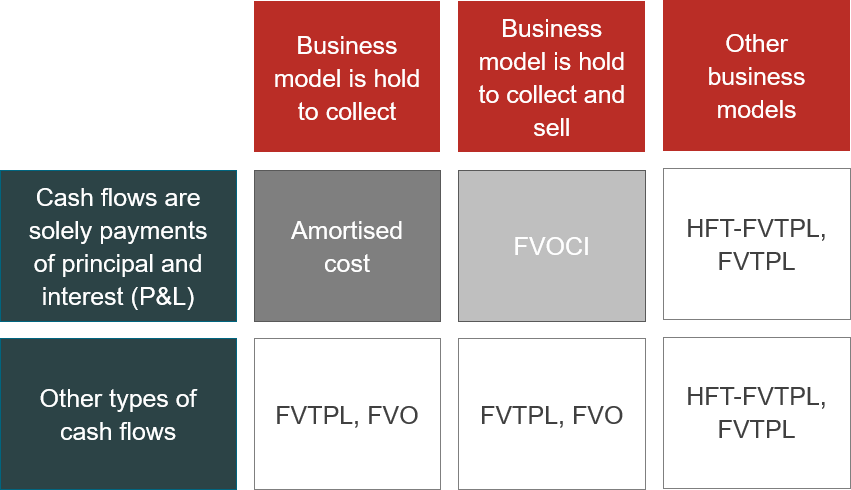
The solution operates with five accounting categories that help to reflect valuation as well as specific disclosure requirements.
The following table shows in total 5 different accounting categories that should be differentiated in accordance with IFRS 9.
The columns show different attributes of the business model and the rows show the necessary differentiation between the characteristics of the cash flows.

Diagram: IFRS 9 accounting categories in the solution
The consideration of 5 different accounting categories supports the assignment of
The assignment of a financial instrument to an accounting category is based on
The diagram below shows the conceptional framework of account classification for financial assets and financial liabilities in the solution.
Based on the combination of an accounting category and the asset side or liability side, the diagram below shows the differentiation, if and how fair value changes related to market prices and fair value changes related to the changes in credit risk are considered in
Diagram 1 refers to the underlying IFRS 9 rules.
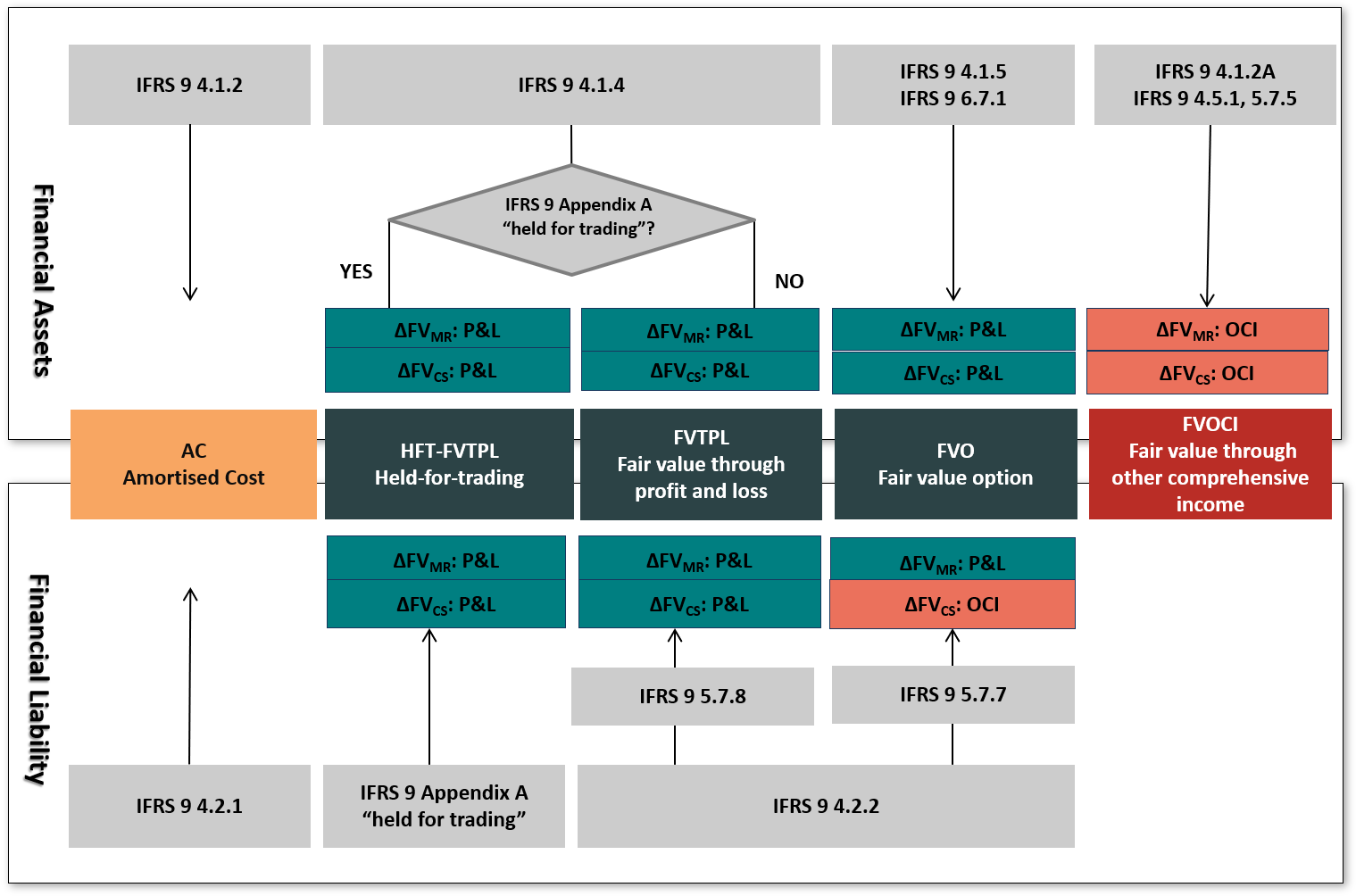
Diagram 1: IFRS 9 accounting category assignment and impact on valuation elements
In general, the classification process requires the analysis of the following questions for each product design:
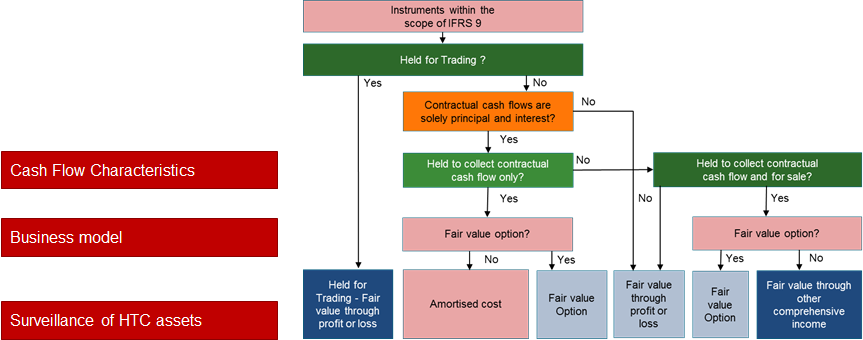
Diagram 2: IFRS 9 category assignment rules
If the assignment of an accounting category changes during the lifecycle of a financial instrument, a reclassification will be triggered.